Fahnenkomplex
In der Mathematik sind Fahnenkomplexe bestimmte Simplizialkomplexe, die in Graphentheorie, Geometrischer Topologie und Geometrischer Gruppentheorie eine Rolle spielen.

Definition
Ein Fahnenkomplex ist ein abstrakter Simplizialkomplex, der die folgende Bedingung ("Gromov's no -condition") erfüllt: wenn eine Menge von Ecken ist, so dass je zwei Ecken aus zu einem gemeinsamen Simplex gehören, dann bilden die Ecken von einen Simplex.
Beispiele
Ein Graph ist ein Fahnenkomplex genau dann wenn gilt. Hierbei bezeichnet die Länge eines kürzesten Kreises in .
-
 Petersen-Graph:
Petersen-Graph: -
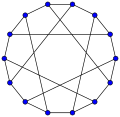 Heawood-Graph:
Heawood-Graph: -
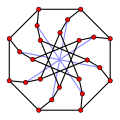 McGee-Graph
McGee-Graph -
 Tutte–Coxeter-Graph
Tutte–Coxeter-Graph
Literatur
- Daniel Wise: From Riches to Raags: 3-Manifolds, Right-Angled Artin Groups, and Cubical Geometry, CBMS Regional Conference Series in Mathematics 2012; 141 pp; softcover, ISBN 0-8218-8800-5
























