DUSP13
| DUSP13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DUSP13, BEDP, DUSP13A, DUSP13B, MDSP, SKRP4, TMDP, dual specificity phosphatase 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 613191; MGI: 1351599; HomoloGene: 121602; GeneCards: DUSP13; OMA:DUSP13 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dual specificity phosphatase 13 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP13 gene.[5]
Function
Members of the protein tyrosine phosphatase superfamily cooperate with protein kinases to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. This superfamily is separated into two families based on the substrate that is dephosphorylated. One family, the dual specificity phosphatases (DSPs) acts on both phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine/threonine residues. This gene encodes different but related DSP proteins through the use of non-overlapping open reading frames, alternate splicing, and presumed different transcription promoters. Expression of the distinct proteins from this gene has been found to be tissue specific and the proteins may be involved in postnatal development of specific tissues. A protein encoded by the upstream ORF was found in skeletal muscle, whereas the encoded protein from the downstream ORF was found only in testis. In mouse, a similar pattern of expression was found. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants were described, but the full-length sequence of only some were determined.[5]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000079393 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021768 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DUSP13 dual specificity phosphatase 13".
Further reading
- Nakamura K, Shima H, Watanabe M, et al. (2000). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dual-specificity protein phosphatase possibly involved in spermatogenesis". Biochem. J. 344 Pt 3 (Pt 3): 819–25. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3440819. PMC 1220704. PMID 10585869.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Deloukas P, Earthrowl ME, Grafham DV, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 10". Nature. 429 (6990): 375–81. Bibcode:2004Natur.429..375D. doi:10.1038/nature02462. PMID 15164054.
- Chen HH, Luche R, Wei B, Tonks NK (2004). "Characterization of two distinct dual specificity phosphatases encoded in alternative open reading frames of a single gene located on human chromosome 10q22.2". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (40): 41404–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405286200. PMID 15252030.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, et al. (2005). "High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells". Science. 307 (5715): 1621–5. Bibcode:2005Sci...307.1621B. doi:10.1126/science.1105776. PMID 15761153. S2CID 39457788.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Kim SJ, Jeong DG, Yoon TS, et al. (2007). "Crystal structure of human TMDP, a testis-specific dual specificity protein phosphatase: implications for substrate specificity". Proteins. 66 (1): 239–45. doi:10.1002/prot.21197. PMID 17044055. S2CID 30555597.
- v
- t
- e
-
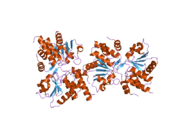 2gwo: crystal structure of TMDP
2gwo: crystal structure of TMDP -
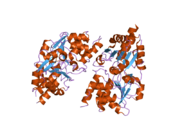 2pq5: Crystal structure of Dual specificity protein phosphatase 13 (DUSP13)
2pq5: Crystal structure of Dual specificity protein phosphatase 13 (DUSP13)
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 10 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e