Nodule of vermis
| Nodule of vermis | |
|---|---|
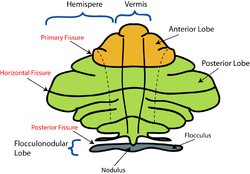 Schematic representation of the major anatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum. Superior view of an "unrolled" cerebellum, placing the vermis in one plane. | |
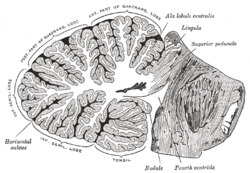 Sagittal section of the cerebellum, near the junction of the vermis with the hemisphere. (Nodule labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodulus vermis |
| NeuroNames | 681 |
| TA98 | A14.1.07.302 |
| TA2 | 5832 |
| FMA | 83882 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
The nodule (nodular lobe), or anterior end of the inferior vermis, abuts against the roof of the fourth ventricle, and can only be distinctly seen after the cerebellum has been separated from the medulla oblongata and pons.
On either side of the nodule is a thin layer of white substance, named the posterior medullary velum.
It is semilunar in form, its convex border being continuous with the white substance of the cerebellum; it extends on either side as far as the flocculus.
Additional Images
- Cerebellum. Inferior surface.
- Cerebellum. Inferior surface.
- Cerebellum. Inferior surface.
External links
- Atlas image: n2a7p4 at the University of Michigan Health System
- https://web.archive.org/web/20010514005529/http://www.ib.amwaw.edu.pl/anatomy/atlas/image_11e.htm
- v
- t
- e
Anatomy of the cerebellum
| Lobes |
|
|---|---|
| Medial/lateral |
|
| Deep cerebellar nuclei | |
|---|---|
| Cerebellar cortex |
|
| Internal |
|
|---|---|
| Peduncles |
 | This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e














