Prednisolone acetate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Prednisolone 21-acetate |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.123 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H30O6 |
| Molar mass | 402.487 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Melting point | 240 °C (464 °F) |
| |
InChI
| |
Prednisolone acetate is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester. It is the 21-acetate ester of prednisolone.[1][2]
Safety
Prednisolone acetate is acutely toxic with an LD50 of >240 mg/kg for a rat and 3500 mg/kg for a mouse. Effects may present delayed. Target organs include adrenal cortex, bones, and eyes. It is also a known teratogen.[3] Class B PPE should be worn when working with this chemical. Any contact with this chemical should be taken seriously and the affected person taken to the hospital.
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose may include altered mental status with psychosis, burning or itching skin, seizures, deafness, depression, dry skin, heart rhythm disturbances, hypertension, increase appetite, increased infection risk, muscle weakness, nausea and vomiting, nervousness, sleepiness, stopping of menstrual cycle, swelling in lower legs, weak bones, weakness, and worsening of health conditions.[4]
Most common route of overdose is via ingestion.[4]
Treatment may involve IV fluids, activated carbon, laxativea, breathing support and additional medications to alleviate symptoms.[4]
Physical properties
Material is a white powder in its pure form. Good solubility in Chloroform, Methanol, and Ethanol. Poorly soluble in water. Melting point of this material is 240 °C.[3] UV-VIS spectroscopy can be used to determine purity and identity, resolving a peak around 244 nm in water.
References
- ^ PubChem. "Prednisolone 21-acetate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- ^ Sousa FJ (October 1991). "The bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness of prednisolone acetate vs. prednisolone sodium phosphate: a 20-year review". The CLAO Journal. 17 (4): 282–4. PMID 1764775.
- ^ a b "Prednisolone 21-acetate P8650". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- ^ a b c "Corticosteroids overdose". MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- v
- t
- e
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoid receptor modulators
- List of corticosteroids
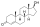 | This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










