Phospholamban
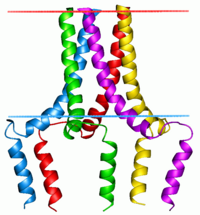 Phospholamban pentamer | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Phospholamban | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF04272 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005984 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1fjk / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.A.50 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 62 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1zll | ||||||||
| Membranome | 383 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| PLN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PLN, CMD1P, CMH18, PLB, phospholamban | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 172405; MGI: 97622; HomoloGene: 136758; GeneCards: PLN; OMA:PLN - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Phospholamban, also known as PLN or PLB, is a micropeptide protein that in humans is encoded by the PLN gene.[5] Phospholamban is a 52-amino acid integral membrane protein that regulates the calcium (Ca2+) pump in cardiac muscle cells.[6]
Function
This protein is found as a pentamer and is a major substrate for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) in cardiac muscle. In the unphosphorylated state, phospholamban is an inhibitor of cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA2)[7] which transports calcium from cytosol into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. When phosphorylated (by PKA) - disinhibition of Ca2+-ATPase of SR leads to faster Ca2+ uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, thereby contributing to the lusitropic response elicited in heart by beta-agonists.[8] The protein is a key regulator of cardiac diastolic function. Mutations in this gene are a cause of inherited human dilated cardiomyopathy with refractory congestive heart failure.[9]
When phospholamban is phosphorylated by PKA, its ability to inhibit SERCA2 is lost.[10] Thus, activators of PKA, such as the beta-adrenergic agonist epinephrine (released by sympathetic stimulation), may enhance the rate of cardiac myocyte relaxation. In addition, since SERCA2 is more active, the next action potential will cause an increased release of calcium, resulting in increased contraction (positive inotropic effect). When phospholamban is not phosphorylated, such as when PKA is inactive, it can interact with and inhibit SERCA. Thus, the overall effect of unphosphorylated phospholamban is to decrease contractility and the rate of muscle relaxation, thereby decreasing stroke volume and heart rate, respectively.[11]
Clinical significance
Gene knockout of phospholamban results in animals with hyperdynamic hearts, with little apparent negative consequence.[12]
Mutations in this gene are a cause of inherited human dilated cardiomyopathy with refractory congestive heart failure.[13][14]
Discovery
Phospholamban was discovered by Arnold Martin Katz and coworkers in 1974.[15]
Interactions
PLN has been shown to interact with SLN[16][17] and SERCA1.[17][18][19]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198523 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038583 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Fujii J, Zarain-Herzberg A, Willard HF, Tada M, MacLennan DH (June 1991). "Structure of the rabbit phospholamban gene, cloning of the human cDNA, and assignment of the gene to human chromosome 6". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 266 (18): 11669–75. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)99009-5. PMID 1828805.
- ^ Rodriguez P, Kranias EG (December 2005). "Phospholamban: a key determinant of cardiac function and dysfunction". Archives des Maladies du Coeur et des Vaisseaux. 98 (12): 1239–43. PMID 16435604.
- ^ "InterPro".
- ^ Hagemann D, Xiao RP (February 2002). "Dual site phospholamban phosphorylation and its physiological relevance in the heart". Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 12 (2): 51–6. doi:10.1016/S1050-1738(01)00145-1. PMID 11852250.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PLN phospholamban".
- ^ Medical Physiology. Philadelphia: Saunders. 2004. ISBN 0-8089-2333-1.
- ^ Brittsan AG, Kranias EG (December 2000). "Phospholamban and cardiac contractile function". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 32 (12): 2131–9. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2000.1270. PMID 11112989.
- ^ Luo W, Grupp IL, Harrer J, Ponniah S, Grupp G, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Kranias EG (September 1994). "Targeted ablation of the phospholamban gene is associated with markedly enhanced myocardial contractility and loss of beta-agonist stimulation". Circulation Research. 75 (3): 401–9. doi:10.1161/01.res.75.3.401. PMID 8062415.
- ^ Schmitt JP, Kamisago M, Asahi M, Li GH, Ahmad F, Mende U, Kranias EG, MacLennan DH, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (February 2003). "Dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure caused by a mutation in phospholamban". Science. 299 (5611): 1410–3. doi:10.1126/science.1081578. PMID 12610310. S2CID 12253445.
- ^ Eijgenraam TR, Boukens BJ, Boogerd CJ, Schouten EM, van de Kolk CW, Stege NM, te Rijdt WP, Hoorntje ET, van der Zwaag PA, van Rooij E, van Tintelen JP, van den Berg MP, van der Meer P, van der Velden J, Silljé HH, de Boer RA (17 June 2020). "The phospholamban p.(Arg14del) pathogenic variant leads to cardiomyopathy with heart failure and is unreponsive to standard heart failure therapy". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 9819. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.9819E. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-66656-9. PMC 7300032. PMID 32555305.
- ^ Tada M, Kirchberger MA, Repke DI, Katz AM (October 1974). "The stimulation of calcium transport in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 249 (19): 6174–80. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42237-0. PMID 4371608.
- ^ Asahi M, Sugita Y, Kurzydlowski K, De Leon S, Tada M, Toyoshima C, MacLennan DH (April 2003). "Sarcolipin regulates sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) by binding to transmembrane helices alone or in association with phospholamban". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (9): 5040–5. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.5040A. doi:10.1073/pnas.0330962100. PMC 154294. PMID 12692302.
- ^ a b Asahi M, Kurzydlowski K, Tada M, MacLennan DH (July 2002). "Sarcolipin inhibits polymerization of phospholamban to induce superinhibition of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPases (SERCAs)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (30): 26725–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200269200. PMID 12032137.
- ^ Asahi M, Kimura Y, Kurzydlowski K, Tada M, MacLennan DH (November 1999). "Transmembrane helix M6 in sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase forms a functional interaction site with phospholamban. Evidence for physical interactions at other sites". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (46): 32855–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.46.32855. PMID 10551848.
- ^ Asahi M, Green NM, Kurzydlowski K, Tada M, MacLennan DH (August 2001). "Phospholamban domain IB forms an interaction site with the loop between transmembrane helices M6 and M7 of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPases". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (18): 10061–6. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9810061A. doi:10.1073/pnas.181348298. PMC 56915. PMID 11526231.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
External links
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Cardiac phospholamban
- v
- t
- e
-
 1fjk: NMR Solution Structure of Phospholamban (C41F)
1fjk: NMR Solution Structure of Phospholamban (C41F) -
 1fjp: NMR Solution Structure of Phospholamban (C41F)
1fjp: NMR Solution Structure of Phospholamban (C41F) -
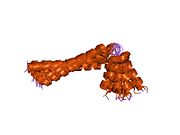 1n7l: Solution NMR structure of phospholamban in detergent micelles
1n7l: Solution NMR structure of phospholamban in detergent micelles -
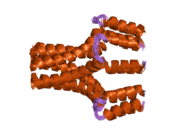 1zll: NMR Structure of Unphosphorylated Human Phospholamban Pentamer
1zll: NMR Structure of Unphosphorylated Human Phospholamban Pentamer