Solar eclipse of January 1, 1889
A total solar eclipse occurred on January 1, 1889. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible across western United States, and central Canada. Partiality was visible across the northern Pacific Ocean including Hawaii, and all of the United States.
Observations and predictions
-
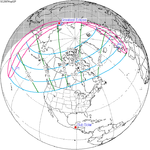
 Path across the western United States and central Canada
Path across the western United States and central Canada -
 Drawing by Mabel Loomis Todd
Drawing by Mabel Loomis Todd -
 Photograph taken from Norman, California
Photograph taken from Norman, California
Impact
Wovoka the Paiute prophet received visions during the solar eclipse of January 1889. These visions were framework for the Pan-Indian religious movement known as the Ghost Dance.[1]
Related eclipses
Saros 120
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 120, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on May 27, 933 AD. It contains annular eclipses from August 11, 1059 through April 26, 1492; hybrid eclipses from May 8, 1510 through June 8, 1564; and total eclipses from June 20, 1582 through March 30, 2033. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 7, 2195. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 11 at 6 minutes, 24 seconds on September 11, 1113, and the longest duration of totality was produced by member 60 at 2 minutes, 50 seconds on March 9, 1997. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[2]
| Series members 50–71 occur between 1801 and 2195: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 51 | 52 |
 November 19, 1816 |  November 30, 1834 |  December 11, 1852 |
| 53 | 54 | 55 |
 December 22, 1870 |  January 1, 1889 |  January 14, 1907 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 |
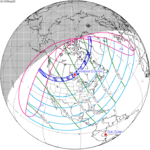
 January 24, 1925 |  February 4, 1943 | 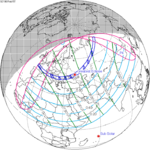 February 15, 1961 |
| 59 | 60 | 61 |
 February 26, 1979 | 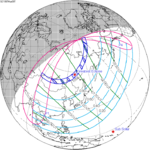 March 9, 1997 | 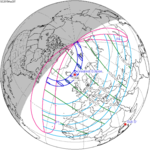 March 20, 2015 |
| 62 | 63 | 64 |
 March 30, 2033 | 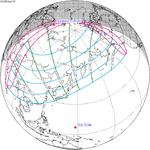 April 11, 2051 |  April 21, 2069 |
| 65 | 66 | 67 |
 May 2, 2087 |  May 14, 2105 |  May 25, 2123 |
| 68 | 69 | 70 |
 June 4, 2141 |  June 16, 2159 |  June 26, 2177 |
| 71 | ||
 July 7, 2195 | ||
References
Further reading
- Holden, E. S. (1889). "On the solar eclipse of January 1, 1889". The Observatory. 12: 130–134. Bibcode:1889Obs....12..130H.
- Holden, E. S. (April 1889). "On the photographs of the corona at the solar eclipse of 1889, January 1". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 49 (6): 343. Bibcode:1889MNRAS..49..343H. doi:10.1093/mnras/49.6.343.
- Lockyer, J. Norman (March 1889). "The Total Solar Eclipse of January 1". Nature. 39 (1012): 487–488. Bibcode:1889Natur..39..487L. doi:10.1038/039487b0. S2CID 4097907.
- Payne, William W. (February 1889). "Total Solar Eclipse, Jan 1, 1889". Sidereal Messenger. 8: 64–68. Bibcode:1889SidM....8...64P.
- Pickering, William H. (August 1889). "The Total Solar Eclipse of January, 1889". Sidereal Messenger. 8: 336.1–339. Bibcode:1889SidM....8..336P.
- Pritchett, H. S. (June 1891). "The Solar Corona of January, 1889, from the Photographs". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 3 (16): 155. Bibcode:1891PASP....3..155P. doi:10.1086/120281. S2CID 123421425.
- Taylor, A. (November 1890). "The total solar eclipse of December 21-22, 1889". The Observatory. 13: 348–351. Bibcode:1890Obs....13..348T.
- Todd, Mabel Loomis (1900). Total Eclipses of the Sun. Little, Brown.
- Upton, Winslow; Rotch, Abbott Lawrence; Pickering, Edward Charles (1893). "Meteorological and other observations made at Willows, California, in connection with the total solar eclipse of January 1, 1889". Annals of the Astronomical Observatory of Harvard College. 29 (1). Cambridge: J. Wilson and Son: 1. Bibcode:1893AnHar..29....1U.
External links
- NASA chart graphics
- Googlemap
- NASA Besselian elements
- Photo of Solar Corona January 1, 1889
- Eclipse of June 1, 1889. Contact print from the original glass negative. Lick Observatory Plate Archive, Mt. Hamilton. [January 1, 1889?!]
- C.E. Watkins photo / eclipse / lick observatory 1889?[permanent dead link], The J. Paul Getty Museum, Object Number: 88.XM.92.83
- v
- t
- e
| By era | |
|---|---|
| Saros series (list) | |
| Visibility | |
| Historical |
|

Total/hybrid eclipses
→ next total/hybrid
- 1133
- 1185
- 1560
- 1598
- 1652
- 1654
- 1673
- 1706
- 1715
- 1724
- 1766
- 1778
- 1780
- 1806
- 1816
- 1824
- 1842
- 1851
- 1853
- 1857
- 1858
- 1860
- 1865
- 1867
- 1868
- 1869
- 1870
- 1871
- 1874
- 1875
- 1878
- 1882
- 1883
- 1885
- 1886
- 1887
- Jan. 1889
- Dec. 1889
- 1893
- 1896
- 1898
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- Jan. 1908
- Dec. 1908
- 1909
- 1910
- 1911
- Apr. 1912
- Oct. 1912
- 1914
- 1916
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1928
- 1929
- Apr. 1930
- Oct. 1930
- 1932
- 1934
- 1936
- 1937
- 1938
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jan. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- 1952
- 1954
- 1955
- 1956
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- 1967
- 1968
- 1970
- 1972
- 1973
- 1974
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1985
- 1986
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1997
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- 2024
- → 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2033
- 2034
- 2035
- 2037
- 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2050
- 2052
- 2053
- 2055
- Jan. 2057
- Dec. 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2068
- 2070
- 2071
- 2072
- 2073
- 2075
- 2076
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- 2086
- 2088
- 2089
- 2090
- 2091
- 2093
- 2094
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100
- 2186

Annular eclipses
→ next annular
- 1820
- 1854
- 1879
- 1889
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- 1908
- 1911
- 1914
- Feb. 1915
- Aug. 1915
- 1916
- 1917
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1929
- 1932
- Feb. 1933
- Aug. 1933
- 1934
- 1935
- 1936
- 1937
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jul. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- Mar. 1951
- Sep. 1951
- 1952
- Jan. 1954
- Dec. 1954
- 1955
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- Mar. 1969
- Sep. 1969
- 1970
- 1972
- Jan. 1973
- Dec. 1973
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- → 2024
- 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2032
- 2034
- 2035
- 2036
- Jan. 2038
- Jul. 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2052
- 2053
- Jan. 2056
- Jul. 2056
- 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2070
- 2071
- Jan. 2074
- Jul. 2074
- 2075
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- Jun. 2085
- Dec. 2085
- 2088
- 2089
- Feb. 2092
- Aug. 2092
- 2093
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100

Partial eclipses
→ next partial
- Jan. 1639
- Apr. 1902
- May 1902
- Oct. 1902
- Feb. 1906
- Jul. 1906
- Aug. 1906
- Dec. 1909
- Nov. 1910
- Apr. 1913
- Aug. 1913
- Sep. 1913
- Dec. 1916
- Jan. 1917
- Jun. 1917
- Jul. 1917
- May 1920
- Nov. 1920
- Mar. 1924
- Jul. 1924
- Aug. 1924
- Dec. 1927
- Jun. 1928
- Nov. 1928
- Apr. 1931
- Sep. 1931
- Oct. 1931
- Jan. 1935
- Feb. 1935
- Jun. 1935
- Jul. 1935
- Nov. 1938
- Mar. 1942
- Aug. 1942
- Sep. 1942
- Jan. 1946
- May 1946
- Jun. 1946
- Nov. 1946
- Apr. 1949
- Oct. 1949
- Feb. 1953
- Jul. 1953
- Aug. 1953
- Dec. 1956
- Mar. 1960
- Sep. 1960
- Jan. 1964
- Jun. 1964
- Jul. 1964
- Dec. 1964
- May 1967
- Mar. 1968
- Feb. 1971
- Jul. 1971
- Aug. 1971
- Dec. 1974
- May 1975
- Nov. 1975
- Apr. 1978
- Oct. 1978
- Jan. 1982
- Jun. 1982
- Jul. 1982
- Dec. 1982
- May 1985
- Apr. 1986
- Mar. 1989
- Aug. 1989
- Dec. 1992
- May 1993
- Nov. 1993
- Apr. 1996
- Oct. 1996
- Sep. 1997
- Feb. 2000
- 1 Jul. 2000
- 31 Jul. 2000
- Dec. 2000
- Apr. 2004
- Oct. 2004
- Mar. 2007
- Sep. 2007
- Jan. 2011
- Jun. 2011
- Jul. 2011
- Nov. 2011
- Oct. 2014
- Sep. 2015
- Feb. 2018
- Jul. 2018
- Aug. 2018
- Jan. 2019
- Apr. 2022
- Oct. 2022
- → Mar. 2025
- Sep. 2025
- Jan. 2029
- Jun. 2029
- Jul. 2029
- Dec. 2029
- 2032
- 2033
- Feb. 2036
- Jul. 2036
- Aug. 2036
- 2037
- May 2040
- Nov. 2040
- Jan. 2047
- Jun. 2047
- Jul. 2047
- Dec. 2047
- 2050
- Apr. 2051
- Oct. 2051
- Mar. 2054
- Aug. 2054
- Sep. 2054
- 2055
- May 2058
- Jun. 2058
- Nov. 2058
- Mar. 2062
- Sep. 2062
- Feb. 2065
- Jul. 2065
- Aug. 2065
- Dec. 2065
- 2068
- Apr. 2069
- May 2069
- Oct. 2069
- 2072
- 2073
- Jun. 2076
- Jul. 2076
- Nov. 2076
- Feb. 2083
- Jul. 2083
- Aug. 2083
- 2084
- 2086
- May 2087
- Jun. 2087
- Oct. 2087
- 2090
- 2091
- Jun. 2094
- Jul. 2094
- Dec. 2094
- Apr. 2098
- Sep. 2098
- Oct. 2098
 Astronomy portal
Astronomy portal Solar System portal
Solar System portal Category
Category
















