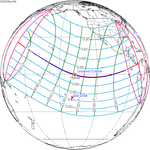
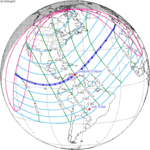
Solar eclipse of September 10, 1923

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Monday, September 10, and Tuesday, September 11, 1923,[1] with a magnitude of 1.043. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.1 days before perigee (on September 12, 1923, at 23:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2]
The path of totality started at the southeastern tip of Shiashkotan in Japan (now in Russia) on September 11, and crossed the Pacific Ocean, southwestern California including the whole Channel Islands, northwestern and northern Mexico, Yucatan Peninsula, British Honduras (today's Belize), Swan Islands, Honduras, and Serranilla Bank and Bajo Nuevo in Colombia on September 10. The eclipse was over 90% in Los Angeles, San Diego, and Santa Barbara on the Southern California coast. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of far east Russia, North America, Central America, the Caribbean, and northern South America.
Viewings

At Santa Catalina Island, off the coast of California, a large group of scientists gathered to observe the eclipse were foiled by clouds, with the Los Angeles Times saying that "nothing of the eclipse was seen save two glimpses that showed the crescent of the sun, a sickly, white watermelon rind with the wavering black moon and a few rags of black clouds fast blotting out the white light":[3]
All day the scientists from Yerkes Observatory of the University of Chicago, from the University of Wisconsin, from Dearborn University, from Drake University and Carleton College, had rehearsed and rehearsed to the counting of the seconds and there they stood now while the moon covered the sun and the world was dark and still, and though the counter counted there was no possibility of taking pictures; no chance of seeing anything but that gray, blue, purple shadow moving across the sky.[3]
Even as late as 11:30 when the eclipse began, the scientists had hopes. They had come thousands of miles, had worked hard, had spent much money, all for a few minutes of clear sky. They had worked in the sweltering sun for weeks and weeks 1302 feet above the sea. There had not been one moment of one day that was not flooded with sunshine. "And surely," said Prof. Edwin Frost of the University of Chicago, "surely we will have these few minutes today."[3]
In Bakersfield, where the last eclipse of the Sun had taken place 123 years earlier, many watched the eclipse from streets, chickens were confused, and "all the astronomical apparatus of Bakersfield" was trained on the eclipse.[4] In New York City the eclipse, while partial, was viewed successfully; in the area of totality, it was "studied by astronomers who [were] depending on it to help them test out Einstein's famous theory of relativity and whether light rays are bent by the attraction of gravity".[5]
A team from the University of Arizona took images of the corona in Puerto Libertad, Sonora, Mexico, on the east coast of the Gulf of California.[6] A team from Sproul Observatory observed it in Yerbanís in eastern Durango state, Mexico.[7]
Eclipse details
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[8]
| Event | Time (UTC) |
|---|---|
| First Penumbral External Contact | 1923 September 10 at 18:14:41.7 UTC |
| First Umbral External Contact | 1923 September 10 at 19:16:26.6 UTC |
| First Central Line | 1923 September 10 at 19:17:19.8 UTC |
| First Umbral Internal Contact | 1923 September 10 at 19:18:13.2 UTC |
| Equatorial Conjunction | 1923 September 10 at 20:30:34.7 UTC |
| Greatest Eclipse | 1923 September 10 at 20:47:29.1 UTC |
| Greatest Duration | 1923 September 10 at 20:47:52.3 UTC |
| Ecliptic Conjunction | 1923 September 10 at 20:52:49.7 UTC |
| Last Umbral Internal Contact | 1923 September 10 at 22:16:55.2 UTC |
| Last Central Line | 1923 September 10 at 22:17:50.4 UTC |
| Last Umbral External Contact | 1923 September 10 at 22:18:45.5 UTC |
| Last Penumbral External Contact | 1923 September 10 at 23:20:20.4 UTC |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Eclipse Magnitude | 1.04302 |
| Eclipse Obscuration | 1.08790 |
| Gamma | 0.51493 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 11h12m32.0s |
| Sun Declination | +05°05'47.3" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'53.2" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 11h13m08.8s |
| Moon Declination | +05°35'11.3" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 16'20.1" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 0°59'57.1" |
| ΔT | 23.3 s |
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| August 26 Descending node (full moon) | September 10 Ascending node (new moon) |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Partial lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 117 | Total solar eclipse Solar Saros 143 |
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1923
- A partial lunar eclipse on March 3.
- An annular solar eclipse on March 17.
- A partial lunar eclipse on August 26.
- A total solar eclipse on September 10.
Metonic
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of November 22, 1919
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 29, 1927
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 30, 1916
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 21, 1930
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of September 4, 1914
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of September 14, 1932
Tritos
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of October 10, 1912
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of August 10, 1934
Solar Saros 143
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 30, 1905
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of September 21, 1941
Inex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of September 29, 1894
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of August 20, 1952
Triad
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of November 9, 1836
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010
Solar eclipses of 1921–1924
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[9]
The partial solar eclipse on July 31, 1924 occurs in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1921 to 1924 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 118 | April 8, 1921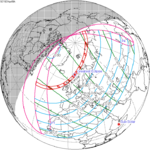 Annular | 0.8869 | 123 | October 1, 1921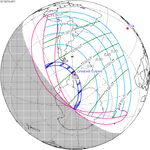 Total | −0.9383 | |
| 128 | March 28, 1922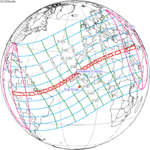 Annular | 0.1711 | 133 | September 21, 1922 Total | −0.213 | |
| 138 | March 17, 1923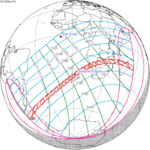 Annular | −0.5438 | 143 | September 10, 1923 Total | 0.5149 | |
| 148 | March 5, 1924 Partial | −1.2232 | 153 | August 30, 1924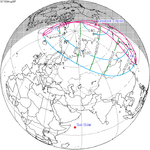 Partial | 1.3123 | |
Saros 143
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 143, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 72 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on March 7, 1617. It contains total eclipses from June 24, 1797 through October 24, 1995; hybrid eclipses from November 3, 2013 through December 6, 2067; and annular eclipses from December 16, 2085 through September 16, 2536. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on April 23, 2897. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 16 at 3 minutes, 50 seconds on August 19, 1887, and the longest duration of annularity will be produced by member 51 at 4 minutes, 54 seconds on September 6, 2518. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[10]
| Series members 12–33 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 13 | 14 |
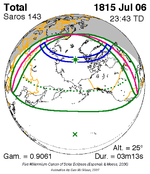 July 6, 1815 |  July 17, 1833 |  July 28, 1851 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 August 7, 1869 |  August 19, 1887 | 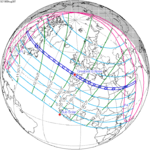 August 30, 1905 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 September 10, 1923 |  September 21, 1941 |  October 2, 1959 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
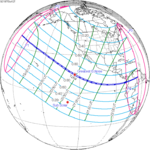 October 12, 1977 | 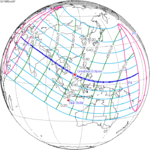 October 24, 1995 | 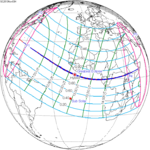 November 3, 2013 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
 November 14, 2031 | 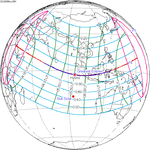 November 25, 2049 |  December 6, 2067 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 December 16, 2085 |  December 29, 2103 |  January 8, 2122 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 January 20, 2140 | 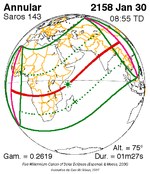 January 30, 2158 |  February 10, 2176 |
| 33 | ||
 February 21, 2194 | ||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 23 eclipse events between February 3, 1859 and June 29, 1946 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| February 1–3 | November 21–22 | September 8–10 | June 28–29 | April 16–18 |
| 109 | 111 | 113 | 115 | 117 |
 February 3, 1859 | 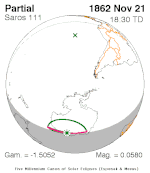 November 21, 1862 |  June 28, 1870 |  April 16, 1874 | |
| 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 | 127 |
 February 2, 1878 |  November 21, 1881 |  September 8, 1885 |  June 28, 1889 |  April 16, 1893 |
| 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 | 137 |
 February 1, 1897 |  November 22, 1900 |  September 9, 1904 |  June 28, 1908 |  April 17, 1912 |
| 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 | 147 |
 February 3, 1916 |  November 22, 1919 |  September 10, 1923 |  June 29, 1927 |  April 18, 1931 |
| 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 | |
 February 3, 1935 |  November 21, 1938 |  September 10, 1942 | 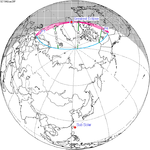 June 29, 1946 | |
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2087 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 August 17, 1803 (Saros 132) |  July 17, 1814 (Saros 133) |  June 16, 1825 (Saros 134) |  May 15, 1836 (Saros 135) |  April 15, 1847 (Saros 136) |
 March 15, 1858 (Saros 137) |  February 11, 1869 (Saros 138) |  January 11, 1880 (Saros 139) |  December 12, 1890 (Saros 140) |  November 11, 1901 (Saros 141) |
 October 10, 1912 (Saros 142) |  September 10, 1923 (Saros 143) | 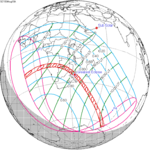 August 10, 1934 (Saros 144) |  July 9, 1945 (Saros 145) |  June 8, 1956 (Saros 146) |
 May 9, 1967 (Saros 147) |  April 7, 1978 (Saros 148) |  March 7, 1989 (Saros 149) |  February 5, 2000 (Saros 150) |  January 4, 2011 (Saros 151) |
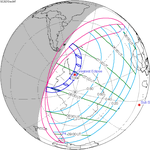 December 4, 2021 (Saros 152) | 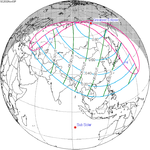 November 3, 2032 (Saros 153) |  October 3, 2043 (Saros 154) |  September 2, 2054 (Saros 155) |  August 2, 2065 (Saros 156) |
 July 1, 2076 (Saros 157) |  June 1, 2087 (Saros 158) | |||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
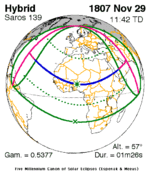 November 29, 1807 (Saros 139) |  November 9, 1836 (Saros 140) |  October 19, 1865 (Saros 141) |
 September 29, 1894 (Saros 142) |  September 10, 1923 (Saros 143) |  August 20, 1952 (Saros 144) |
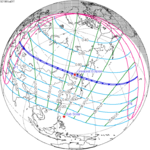 July 31, 1981 (Saros 145) |  July 11, 2010 (Saros 146) | 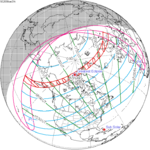 June 21, 2039 (Saros 147) |
 May 31, 2068 (Saros 148) |  May 11, 2097 (Saros 149) |  April 22, 2126 (Saros 150) |
 April 2, 2155 (Saros 151) |  March 12, 2184 (Saros 152) | |
Notes
- ^ "September 10, 1923 Total Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 2 August 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 2 August 2024.
- ^ a b c "SUN'S FROLIC PRIVATE". The Los Angeles Times. Los Angeles, California. 1923-09-11. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Moon's welcome shadow falls across face of September sun". Bakersfield Morning Echo. Bakersfield, California. 1923-09-11. p. 1. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Sun in Eclipse, Seen on Academy Roof, Looks Like Nicked Cheese". Times Union. Brooklyn, New York City. 1923-09-11. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "1923 Solar Eclipse Expedition". Photographic Archive. University of Chicago. Archived from the original on 20 October 2020.
- ^ Miller, John Anthony; Marriott, Ross Walter (1925). "Observations of the total solar eclipse of September 10, 1923". Archived from the original on 28 August 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Total Solar Eclipse of 1923 Sep 10". EclipseWise.com. Retrieved 2 August 2024.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 143". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Google interactive map
- Besselian elements
- Foto and sketchs of Solar Corona September 10, 1923
- v
- t
- e
| By era | |
|---|---|
| Saros series (list) | |
| Visibility | |
| Historical |
|

Total/hybrid eclipses
→ next total/hybrid
- 1133
- 1185
- 1560
- 1598
- 1652
- 1654
- 1673
- 1706
- 1715
- 1724
- 1766
- 1778
- 1780
- 1806
- 1816
- 1824
- 1842
- 1851
- 1853
- 1857
- 1858
- 1860
- 1865
- 1867
- 1868
- 1869
- 1870
- 1871
- 1874
- 1875
- 1878
- 1882
- 1883
- 1885
- 1886
- 1887
- Jan. 1889
- Dec. 1889
- 1893
- 1896
- 1898
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- Jan. 1908
- Dec. 1908
- 1909
- 1910
- 1911
- Apr. 1912
- Oct. 1912
- 1914
- 1916
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1928
- 1929
- Apr. 1930
- Oct. 1930
- 1932
- 1934
- 1936
- 1937
- 1938
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jan. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- 1952
- 1954
- 1955
- 1956
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- 1967
- 1968
- 1970
- 1972
- 1973
- 1974
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1985
- 1986
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1997
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- 2024
- → 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2033
- 2034
- 2035
- 2037
- 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2050
- 2052
- 2053
- 2055
- Jan. 2057
- Dec. 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2068
- 2070
- 2071
- 2072
- 2073
- 2075
- 2076
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- 2086
- 2088
- 2089
- 2090
- 2091
- 2093
- 2094
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100
- 2186

Annular eclipses
→ next annular
- 1820
- 1854
- 1879
- 1889
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- 1908
- 1911
- 1914
- Feb. 1915
- Aug. 1915
- 1916
- 1917
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1929
- 1932
- Feb. 1933
- Aug. 1933
- 1934
- 1935
- 1936
- 1937
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jul. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- Mar. 1951
- Sep. 1951
- 1952
- Jan. 1954
- Dec. 1954
- 1955
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- Mar. 1969
- Sep. 1969
- 1970
- 1972
- Jan. 1973
- Dec. 1973
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- → 2024
- 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2032
- 2034
- 2035
- 2036
- Jan. 2038
- Jul. 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2052
- 2053
- Jan. 2056
- Jul. 2056
- 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2070
- 2071
- Jan. 2074
- Jul. 2074
- 2075
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- Jun. 2085
- Dec. 2085
- 2088
- 2089
- Feb. 2092
- Aug. 2092
- 2093
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100

Partial eclipses
→ next partial
- Jan. 1639
- Apr. 1902
- May 1902
- Oct. 1902
- Feb. 1906
- Jul. 1906
- Aug. 1906
- Dec. 1909
- Nov. 1910
- Apr. 1913
- Aug. 1913
- Sep. 1913
- Dec. 1916
- Jan. 1917
- Jun. 1917
- Jul. 1917
- May 1920
- Nov. 1920
- Mar. 1924
- Jul. 1924
- Aug. 1924
- Dec. 1927
- Jun. 1928
- Nov. 1928
- Apr. 1931
- Sep. 1931
- Oct. 1931
- Jan. 1935
- Feb. 1935
- Jun. 1935
- Jul. 1935
- Nov. 1938
- Mar. 1942
- Aug. 1942
- Sep. 1942
- Jan. 1946
- May 1946
- Jun. 1946
- Nov. 1946
- Apr. 1949
- Oct. 1949
- Feb. 1953
- Jul. 1953
- Aug. 1953
- Dec. 1956
- Mar. 1960
- Sep. 1960
- Jan. 1964
- Jun. 1964
- Jul. 1964
- Dec. 1964
- May 1967
- Mar. 1968
- Feb. 1971
- Jul. 1971
- Aug. 1971
- Dec. 1974
- May 1975
- Nov. 1975
- Apr. 1978
- Oct. 1978
- Jan. 1982
- Jun. 1982
- Jul. 1982
- Dec. 1982
- May 1985
- Apr. 1986
- Mar. 1989
- Aug. 1989
- Dec. 1992
- May 1993
- Nov. 1993
- Apr. 1996
- Oct. 1996
- Sep. 1997
- Feb. 2000
- 1 Jul. 2000
- 31 Jul. 2000
- Dec. 2000
- Apr. 2004
- Oct. 2004
- Mar. 2007
- Sep. 2007
- Jan. 2011
- Jun. 2011
- Jul. 2011
- Nov. 2011
- Oct. 2014
- Sep. 2015
- Feb. 2018
- Jul. 2018
- Aug. 2018
- Jan. 2019
- Apr. 2022
- Oct. 2022
- → Mar. 2025
- Sep. 2025
- Jan. 2029
- Jun. 2029
- Jul. 2029
- Dec. 2029
- 2032
- 2033
- Feb. 2036
- Jul. 2036
- Aug. 2036
- 2037
- May 2040
- Nov. 2040
- Jan. 2047
- Jun. 2047
- Jul. 2047
- Dec. 2047
- 2050
- Apr. 2051
- Oct. 2051
- Mar. 2054
- Aug. 2054
- Sep. 2054
- 2055
- May 2058
- Jun. 2058
- Nov. 2058
- Mar. 2062
- Sep. 2062
- Feb. 2065
- Jul. 2065
- Aug. 2065
- Dec. 2065
- 2068
- Apr. 2069
- May 2069
- Oct. 2069
- 2072
- 2073
- Jun. 2076
- Jul. 2076
- Nov. 2076
- Feb. 2083
- Jul. 2083
- Aug. 2083
- 2084
- 2086
- May 2087
- Jun. 2087
- Oct. 2087
- 2090
- 2091
- Jun. 2094
- Jul. 2094
- Dec. 2094
- Apr. 2098
- Sep. 2098
- Oct. 2098
 Astronomy portal
Astronomy portal Solar System portal
Solar System portal Category
Category















